Commissioning and startup
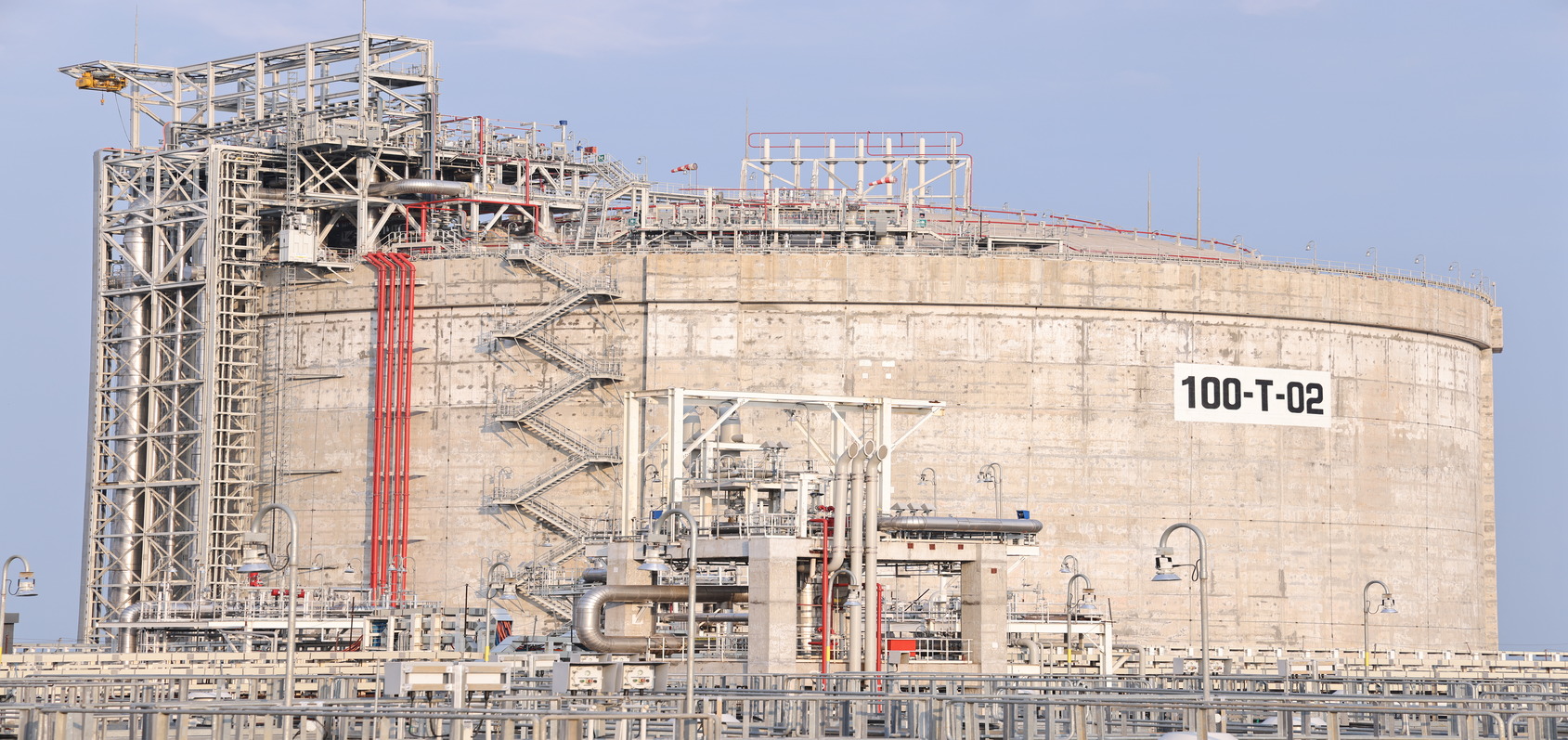
The Qatari vessel ‘Milaha Ras Laffan’ berthed at Dhamra LNG Terminal 1 April 2023 which is also Utkal Divas – the day in 1936 when state of Odisha was formed. This marks the terminal’s commencement of the terminal’s commissioning, which was completed on 6 May 2023.
Features of Dhamra Terminal
| Project Elements | Details |
|---|---|
| Terminal Capacity | 6.5 mtpa (peak capacity)/5 mtpa (nominal capacity), expandable to 10 mtpa |
| Nature of Port | All weather port |
| Storage Tanks | 2, 180,000 m3 each |
| Regasification type and capacity | Shell & Tube Vaporisers (STV) using ambient air |
| Jetty | Compatible for vessels ranging from 40,000 m3 to 265,000 m3 |
| Unloading and Evacuation | 3 unloading arms and 1 vapour return arm |
| Break bulk and Small Scale | Terminal designed for truck loading and re-loading facilities |
| Power System | 3 Gas Engine Generators ( 9.65 MW each) |
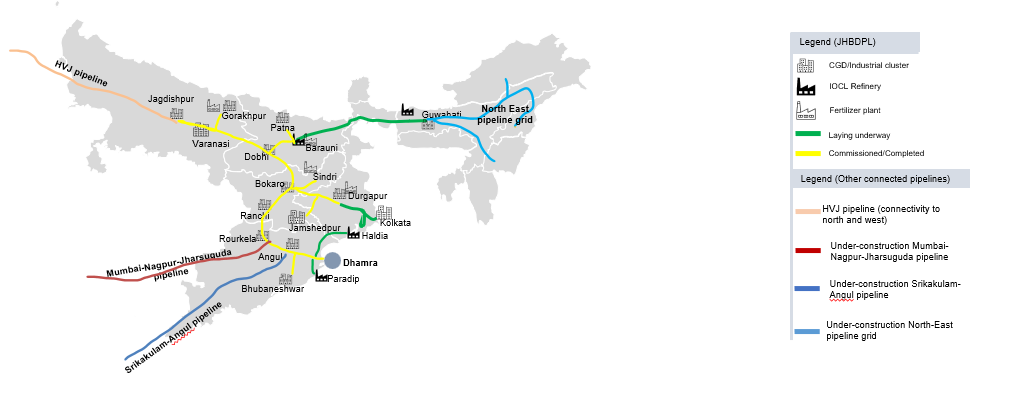
| Pipeline connectivity | Connected to Jagdishpur-Haldia-Bokaro-Dhamra Pipeline (JHBDPL) |
Regas Process
Operations at the terminal can be divided into five major parts:
- Vessel unloading
- Storage
- Recondensing
- Regasification
- Distribution
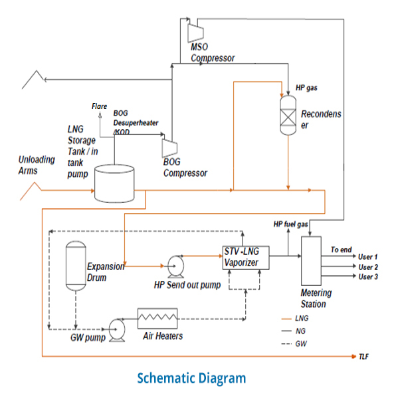
Vessel unloading:
After the vessel is anchored at the jetty head, LNG is offloaded using 3 unloading arms located at the harbour. LNG is received at extremely low/cryogenic temperatures (-160°C). The LNG passes through the cryogenic pipelines that joins the arm to the tanks.
Storage:
Tanks are designed for storing LNG at the temperature received - -160°C. These are double walled insulated tanks. The outer walls are made of reinforced concrete to attain a high level of insulation to minimize LNG boil off. Despite such high insulation, minor evaporation still takes place because of heat leakage. Boil-off Gas (BOG) and Minimum send out (MSO) Compressors are used to manage the gas generated from the heat leakage.
Recondensing:
Located between the LNG in-tank pumps and LNG High Pressure (HP) Pumps, is the Recondenser, serving the purpose of handling BOG at low pressures which otherwise would have required expensive re-liquefaction and high-pressure compression. It feeds recondensed boil-off gas (BOG) to the regasification unit in addition to a stream of liquefied natural gas (LNG). Further, it also serves the purpose of a suction vessel for LNG HP pumps.
The equipment consists of stainless-steel packing bed wherein LNG is dispersed to create a direct & co-current contact with Boil Off Gas, followed by its condensation and reincorporation into the LNG. The recondenser has been also provided with a flow ratio controller, to handle the ratio of BOG to LNG flow for stable operation of the equipment. The recondenser along with BOG handling system are designed for a send out of up to 10 mtpa from the terminal.
Regasification:
This process involves converting Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) to Natural Gas (gaseous). Heat exchanger/STVs are used to regasify the LNG. In this system aqueous Glycol solution (GW) is used as heat exchange medium.
Distribution:
After regasification, natural gas is metered & distributed through the pipeline transmission system.
Pipeline Connectivity
Product & Services Offered
The Dhamra terminal will be the second LNG import terminal being built on India’s east coast. In its first phase, this project will add approximately ~11% to the country’s import capacity and will help diversify the location of gas imports in the country with corresponding strategic and geo-political implications.
The Dhamra is the gateway to gas supplies Eastern and North Eastern India and will help achieve India’s vision of a gas based economy. It will be connected to Jagdishpur -Haldia -Bokaro- Dhamra pipeline (JHBDPL) helping serve new markets. Natural Gas from this terminal will be an important gas supply source to the Pradhan Mantri Urja Ganga (JHBDPL) Project.
The Dhamra terminal offers Regassification services for short and long term contracts based on bilateral agreements.
